Study Area
Study area lies in south east Bastar District of Madhya Pradesh. The greater part of the Bastar district is a plateau, about 600 m. high, leaving a narrow low-land margin on the north and south. The Indravati river which bisects the district into two nearly equal halves and the Sabari river which flows along the south-eastern boundary flow into the Godavari river basin.
Around 66% area of Bastar district is forested. The river Indravati rises from the eastern ghats and enters the district from Orissa State. It flows,east-west through the middle of the district and then turns a sharp bend travelling south and forming interstate boundary between Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, before joining Godavari near Bhopalpattnam. Its total course is 385 km.
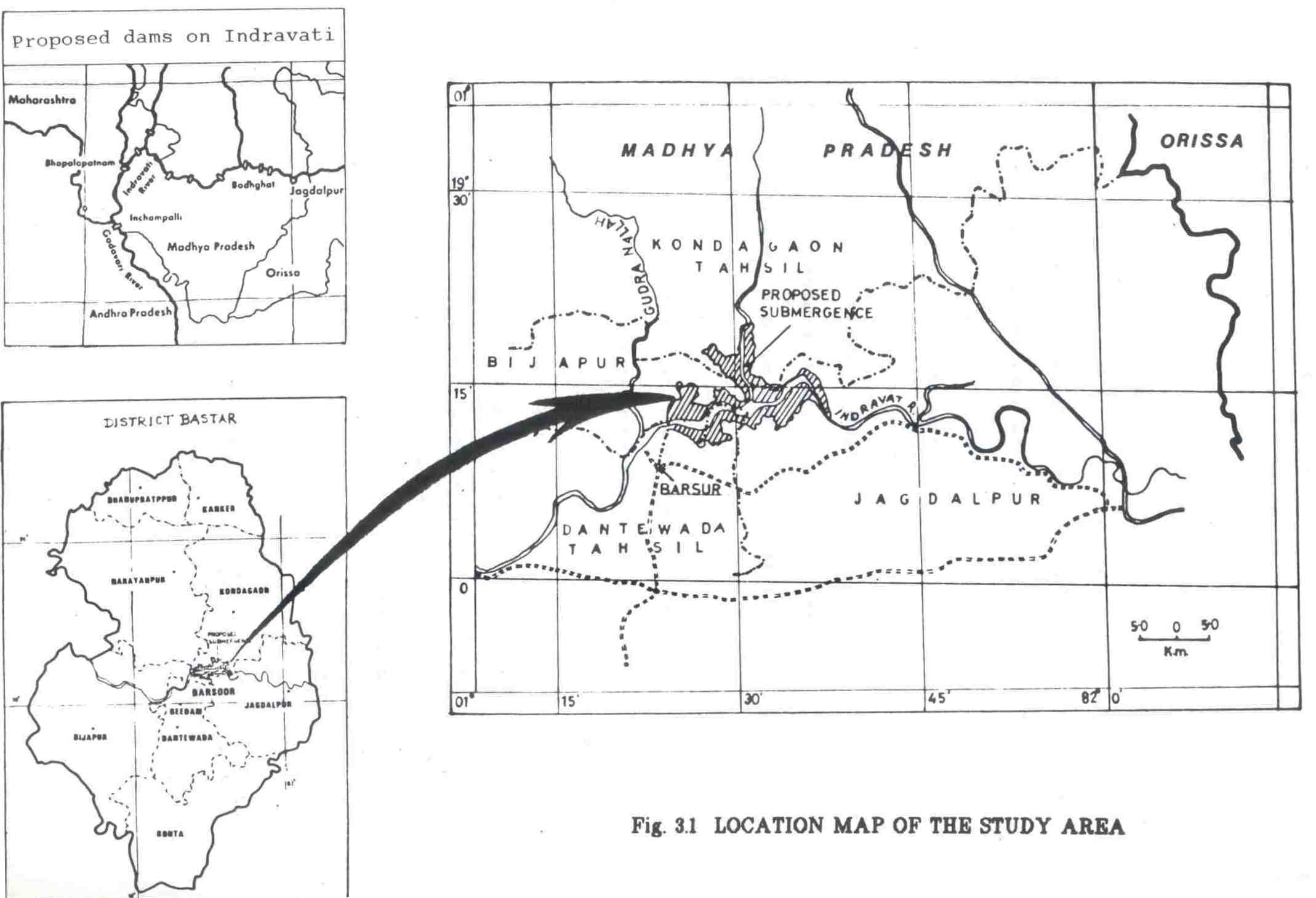
The study was conducted in the submergence area and the construction sites of Indira Sarovar Hydroelectric Project and the nearby impact areas outside the submergence zone. The total area that is affected by the proposed project is 13783.147 ha. Indira Sarovar Project which is a major hydel power project on Indravati is located near the village Barsoor 100 km. from Jagdalpur town, headquarters of .Bastar District. The project site is at latitude 19012' and longitude 81024' (Fig.3.1).
Geology
The common rocks are granites with granitoid gneiss, sandstone and laterites. Lateritic soil and alluvial soil mainly occur in the area. The texture of the soil varies from sandy to fine textured clayey soils. The primary laterites are found as a cap on the top of the trap and gneissic rocks. Secondary laterites are usually found in the valleys and low-lying places. These soils are of fine texture and darker hues and are rich in humus. The river banks of Indravati arid its tributaries have deposits of fertile alluvial soils.
Climate
The climate of the area is monsoonal with a prolonged dry period. There are three distinct seasons and a small post monsoon season, lasting for a month.
(i) Summer Season -Summers are quite hot and stretch from the beginning of March to the middle of June.
(ii) Monsoon Season- It commences from the middle of June and continues till the end of September.
(iii) Monsoon Season - It remains during the month of October.
(iv) Winter Season -It commences from beginning of November and lasts till the end of February.
Temperature
(v) Mean daily temperature of Bastar varies from 19.00C during December to 31.20C in May with a range of 12.1 and the mean annual temperature of 25.350 c.
(vi) Mean daily maximum temperature varies from 26.70C during December to 38.10C in May, i.e. with a range of 11.40C and the mean annual temperature is 31.290C. The hottest months with a mean daily maximum temperature of over 350C are April and May.
(vii) Mean daily minimum temperature varies from 11.50C during December to 24.40C in May with a range of 12.90C and the mean annual of 19.420C. The cool months with mean daily temperature of less than 15.00C December to February. (Data on temperature is based on forty years record of meteorological station of Jagdalpur).
Rainfall
The rainy season starts by about the middle of June and lasts upto the end of September. The total period of rains is 3 1/2 months. The mean total amount of rainfall during the rainy is 1222.8 mm, which is 80.64% of the mean annual rainfall. These figures have been obtained from meteorological station situated at Jagdalpur.
The mean annual Ranfagni is 1516.31 mm, with fluctuations ranging from 1095.6 mm in year 1950 to 2079.5 mm in the year 1975. The main rainy months are July and August with a total mean rainfall of 735.2 mm. which is 48.48% of the annual rainfall. The post rain period lasts for one month i.e. October. It records a sudden drop in rain amount, yet the humid conditions prevail. The mean rainfall during post monsoon period is 102.0 mm. During winter season i.e. during four months commencing from November to February the total mean rainfall is 51.7 mm, which is 3.40% of the total annual rainfall.
Vegetation
The vegetation of Bastar is represented by southern mixed, moist deciduous forests of central India. The botany represents an interesting feature as the southern limit of Sal is reached about 18030' north. The area is predominantly Sal bearing. Other principal miscellaneous species are Pterocarpus marsupium, Terminalia tomentosa, Adina cordifolia and Anogeissus latifolia.
According to revised classification of forest types by Champion and Seth, the forest types of the study area are classified as under:
1) 3C.C2.e (iii)-2) Moist peninsular valley Sal.
2) 3B. /C2-Southern Moist Mixed Deciduous forest.
The total area of land falling under submergence and in construction area is 13783.147 ha. Comprising of forest revenue and private lands as under:
|
Forest Land |
Revenue land |
Private land |
Total (ha) |
|
|
Reservoir Submergence |
5433.862 |
2708.427 |
4698.188 |
12840.477 |
|
Construction area |
270.470 |
360.101 |
312.099 |
942.670 |
|
5704.332 |
3068.528 |
5010.287 |
13783.147 |
The total area of forest land required, for the project is 5704.332 ha and this comprises of areas under Reserved Forests, Protected Forests and undemarkated lands generally known as Orange areas.
The project affects 42 villages, of these 28 villages will be fully submerged and 5 only partially submerged. In another 5 villages, only some lands will get submerged. The remaining 4 villages are deserted forest villages. The total population affected will be 8775 out of which 6209 (70.8%) belonging to scheduled tribes, 733 (8.4%) to scheduled casts and rest 1833 to other communities. Total 1748 families are to be displaced including 1109 land owing and 639 landless families.
Last Updated: October 3, 2015









