Cement plant site
|
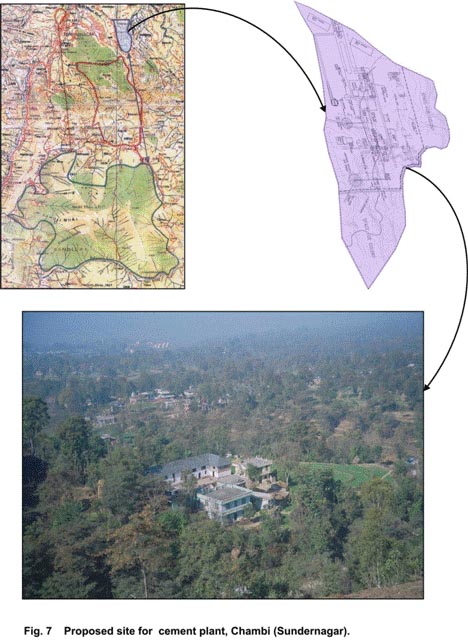
Land-use pattern: The proposed site for the cement plant would occupy an area of 99.27 ha. The present land-use of the area is predominantly cultivation interspersed with four village settlements, namely, Khatarwad, Barodi, Gangal and Chambi. (Fig. 7) Under the existing landuse pattern, agricultural land supports the production of mainly food grain crops primarily for providing subsistence for the villages. Annually, two main cropping seasons of kharif and rabi are followed in the crop rotation cycle. The kharif crop is sown with the onset of monsoon in the area with paddy being the major crop along with certain other crops such as maize and urad. Wheat is the chief rabi crop grown over the winter season and is harvested in April. Vegetable crops such as capsicum, brinjal, tomatoes, chillies and ginger are also grown. Among the plantations for horticulture, major species include mango (Mangifera indica), and amla (Emblica officinalis). As per the proposed site plan for cement plant (Fig. 4) the development in this area would envisage setting up of infrastructure and utilities for cement production. These would include setting up of a conveyor belt for bringing in limestone, specific production units such as raw mill, blending silo, rotary kiln, clinker silo and the cement storage facilities.
Conservation value: The proposed site for the setting up of the cement plant and ancillary facilities at Chambi holds importance in terms of the agro-diversity and associated floral and faunal values including wildlife such as small mammals and avifauna that use cropland habitats. |
Last Updated: October 5, 2015